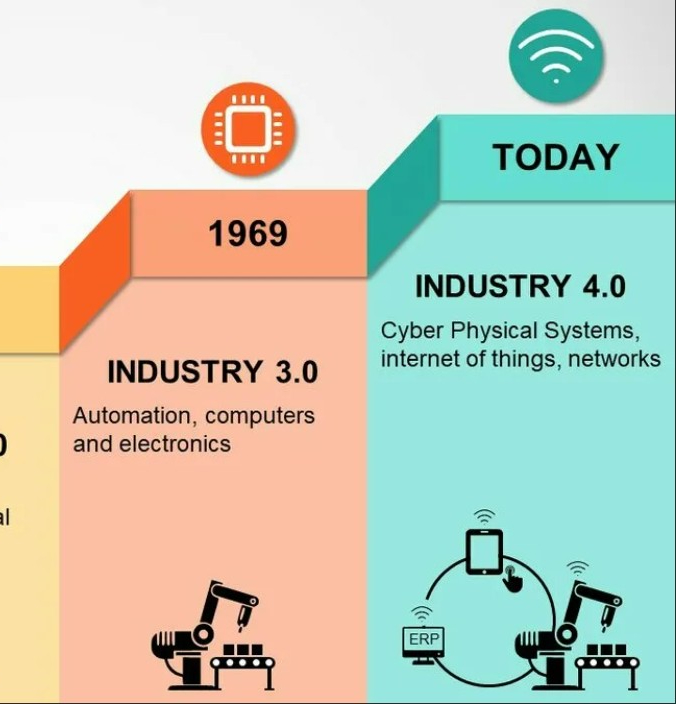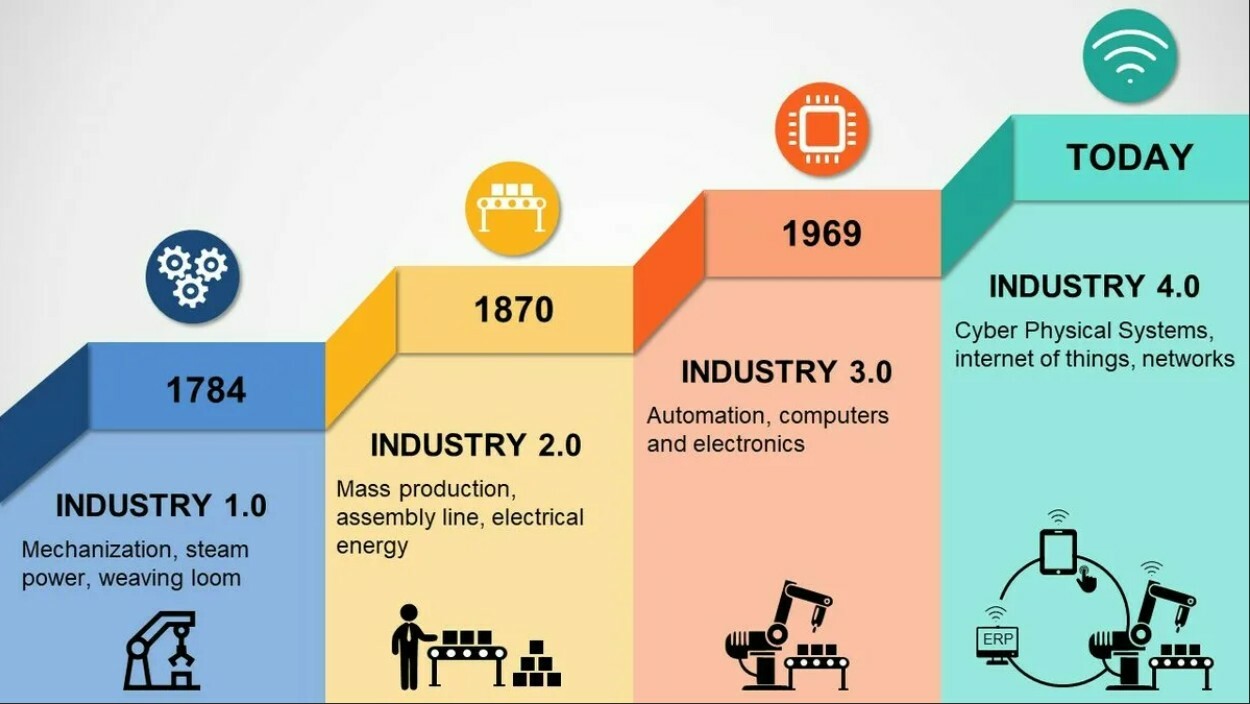
What do we know about Industry 4.0?
Wikipedia defines the term Industry 4.0 as follows:
as “The Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR, or Industry 4.0, conceptualizes rapid change to technology, industries, and societal patterns and processes in the 21st century due to increasing interconnectivity and smart automation. …” which became a logical continuation of industrial improvement from 1784 up to nowadays.
Industry 4.0 is unimaginable without technologies such as the Internet of Things, computer vision, and artificial intelligence which modern IT companies are integrating into production to increase automation, improve communication and self-control, as well as to analyze and diagnose problems without the need for human intervention. That technologies create a manufacturing, which is called smart.
Smart manufacturing is a digital manufacturing enterprise that uses connected devices, machines and production systems to continuously collect and exchange data. The data obtained is subsequently used to justify decisions regarding improvement of processes and to promptly solve emerging problems.
Technologies of "smart manufacturing"
The practice of smart manufacturing is based on various technologies, but the main ones are:- artificial intelligence (AI),
- machine (computer) vision,
- big data analytics (bigData),
- industrial Internet of Things (IoT).
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the backbone of any smart manufacturing.
Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and neural networks is the ability of a computer to perform tasks and make decisions that have historically required a certain level of human intelligence.
Nowadays, if the human eye can recognize something, then so can a neural network. In fact, even more can be done, since machine vision cameras are much more advanced than the human eye.
In order for the machine to learn how to solve manufacturing problems, it must be trained.
How? It is necessary to achieve a high level of generalizing ability on training examples so that the desired objects are stably recognized when they change. That is, if you want the computer to detect defects, you need to “show” these defects to it or, in other words, enter them into the database.
Tasks that artificial intelligence copes with: Detection

Detection of the desired object in the image. There is a picture and it is necessary to find objects of predetermined classes on it. The most common object recognition method is to match image templates to determine if a given object is in the image and, if so, where it is in the image.
Tasks that artificial intelligence copes with: classification - assigning objects to a particular class
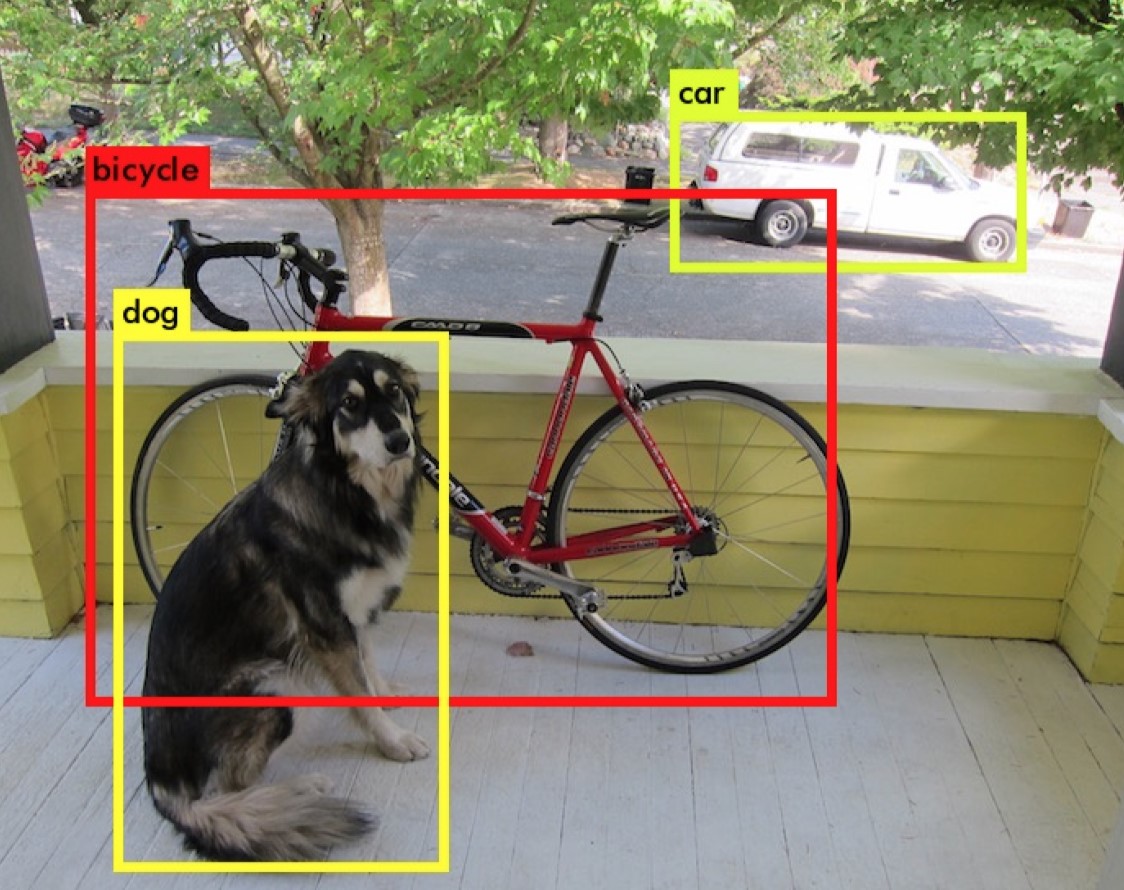
comparing two or more images when searching for images of unique objects, for example, as in the photo - a dog, a bicycle and a car - and assigning these objects to certain classes (cars, animals, furniture, people's faces).
Tasks that artificial intelligence copes with: segmentation - detection of an object on a photo pixel by pixel.
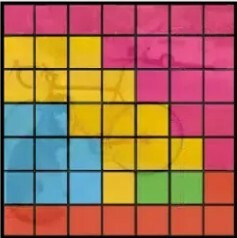
What production tasks does artificial intelligence solve?
- Real-time image analysis for the purposes of product quality control;
- demand planning and forecasting based on artificial intelligence;
- evaluation of images of components on the production line for detection of deviations from quality standards in real time;
- improving workplace safety.
That ability and fast learning allows us to use AI in manufacturing processes to detect the defects of products.
We train the system to detect the surface of pavement bricks and signal about the defects.The more types of defects you will show the system, the faster the system will learn.
This is the function which quality control systems, which implement on a conveyor line, based on.
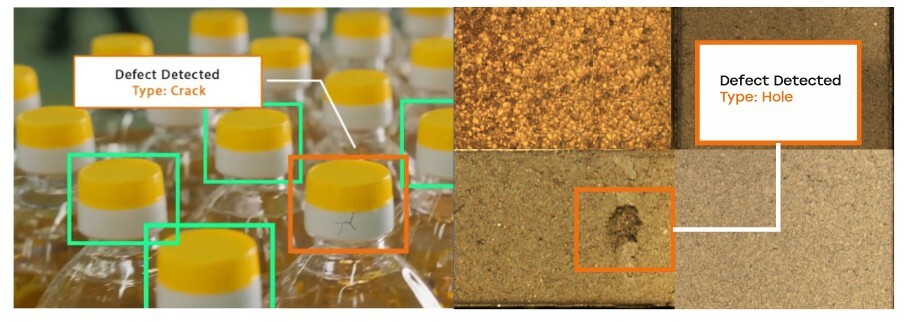
Artificial intelligence recognizes the defects such as cracks on the bottles or holes on the pavement bricks. We can use that technology in different type of plants to identify problems with products and take action to prevent manufacturing of defective products.